Linear Guides: Everything Beginners Need to Know
Why Linear Guides?
In modern industrial manufacturing and automated productions, linear guide rails and blocks have been key linear motion components in achieving precise linear motion. Understanding linear guideway is not only a compulsory course for mechanical engineers or designers but also a basic knowledge that equipment procurement and maintenance personnel need badly. The reasons are mainly reflected in the following aspects:
First, Linear guides is a core determinant of equipment performances. Accuracy, rigidity, and friction characteristics of linear guide rails directly determine the processing accuracy, operational stability and service life of equipment. For CNC machine tools, 3D printers or automation equipment, whether the selection of guide rails is reasonable is often the key to whether product quality can meet the standard.
Second, since linear guide rail and block is with rolling friction, no of sliding one, the friction coefficient is lower, significantly reducing energy consumption, and achieving higher speed and smoother operation. This feature not only improves the machinery efficiency but also reduces long-term operating automated production costs.
Third, common core components for multiple industries linear guides can be in almost all industries that require precise linear motion: from CNC machine, industrial robots to laboratory instruments and 3D printer. Mastering clearly principles and applications of guide rails helps quickly understand and optimize the structure of different types of equipment.
Fourth, cost of wrong linear guide rails selection is higher beyond imagination. Linear guide rails are precision components, and once improperly selected, equipment vibration, reduced accuracy, shortened life, and even the shutdown of the whole machine will largely and frequently occur. For manufacturers, it absolutely increases maintenance costs and after-sales risks; For users, this means a decrease in production efficiency and product quality.
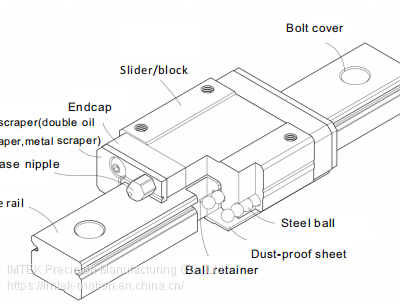
Key Components of a Linear Guides System
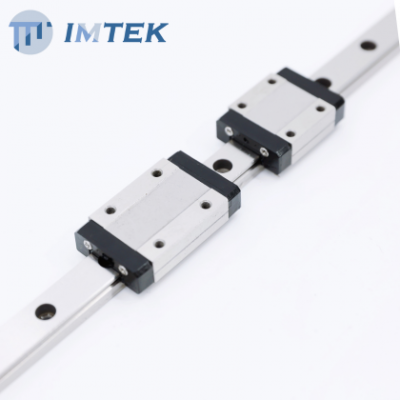
Rail (Linear Guide Rail), the fixed foundation of the system. It defines the direction of movement and provides support for the sliding block. Generally, rails are made of hardened steel, ground to tight tolerances, ensuring both strength and dimensional stability under heavy loads.
Linear Guide Block or Linear Guide Carriage,travel along the rail. Inside the block, rolling elements such as balls or rollers circulate continuously. The design of the block directly impacts load capacity, smoothness of motion, and the ability to maintain high precision under different working conditions.
Rolling Elements (Steel Ball or Roller), the heart of system. Linear ball guides are widely applied in high-speed applications, providing lower friction and high accuracy. Roller type linear guideway is with larger contact area, high rigidity and load capacity, quite suitable for heavy duty CNC machines and industrial automation.


By combining linear guide rail, block and rolling elements into a closed linear motion system, linear guides achieve:
High positioning accuracy, which is essential for precision cutting, measuring and assembly applications.
Low friction coefficient, enabling smooth linear motion with minimal energy loss.
Excellent load capacity and rigidity, allowing equipment to run reliably even under demanding conditions.
Common Application
Linear guide rails are found in nearly all industries that require precise linear motion:
CNC Machining Center: Relies on the high precision and rigidity of linear guides to ensure precise cutting and efficient machining of parts.
Automated equipment and assembly lines: Achieve high-speed and high-stability material handling and positioning.
3D Printers vs. Laser Cutters: The smoothness of the guide rail determines the precision of the print path or cutting trajectory.
Medical and testing equipment: such as imaging diagnostic equipment and precision measuring instruments, which require extremely high linear motion accuracy.

Many beginners make mistakes when want to select suitable linear guides:
Focusing only on linear guide rail price while ignoring key factors(accuracy, load capacity, and service life). In high temperature, dusty or humid conditions, choose stainless steel linear guides or models with sealing protection.
Overlooking the working environment.
Confusing ball type and roller type: linear ball guides are better for high-speed, medium-load use while roller linear guides are suitable for heavy load and high rigidity applications.
Guidance Tips:
If you want to select the correct linear guides for your machines:
First, define the application clearly (speed, load, stroke, environment).
Second, choose the right grade and preload according to precision requirements.
Third, refer to a reliable linear guides catalogue and consult suppliers for professional advice.

Understand Different Types of Linear Guides
1.Linear Guide Universe: Types and Strengths
1.1 Linear Ball Guides
Also called ball type linear guides, they use rolling steel balls for precision motion. IMTEK’s ball guides, heavy duty typr TOH series, flange type TOW series and low profile TTH/TTW series, are good at delivering micron-level positional accuracy, smooth, low-friction movement, and multi-directional load support thanks to the four-point Gothic-arch contact design. Ideal for CNC machines, inspection systems, and robotics, these guides strike the right balance between speed and rigidity.
1.2 Linear Roller Guides
When you need extra rigidity and load capacity, roller type linear guides are your go-to. IMTEK’s TZH-CA/HA (square type) and TZW-CA/HA (flange type, normal/extended length) models replace balls with rollers. This design enhances heavy load handling, torsion resistance, and extends service life under demanding industrial conditions. A reliable choice for high-speed automation where both accuracy and durability matter.
1.3 Miniature Linear Guides
IMTEK Miniature linear guides, designed for compact spaces, such as TGN-C/H (standard size), TGW-C/H (wide size) and stainless steel versions, offer high precision performance where real working condition is limited. Whether building a miniature CNC machine, lab equipment or optical inspection systems, miniature linear guides provide you with the same core benefits—alignment, smoothness, and compact efficiency.
2.Material Variants: Match Guide to Different Working Condition
Alloy steel (S55C, 50CrMo4, SCM420H): Commonly used in TOH and TTH series, these materials deliver high rigidity and machining performance.
>Stainless steel(440c): Built for corrosive, hygienic, or harsh environments, the stainless miniature rail options ensure long-lasting performance even under challenging conditions.
3.Precision Grades & Preload: Fine-Tuning Performance
IMTEK linear guides are available in precision classes like C, H, P, SP, and UP. We can also offer you customized preloads for your operating demands: light preload for high-speed, light-load applications; heavier preload for low-speed, heavy-load systems to enhance high rigidity of the systems. This kind of adaptability ensures you that the linear motion parts can be optimized for repeatability, vibration control, or longevity, depending on your application.
Conclusion Toward More Efficient Linear Motion Systems
Linear guides are more than just machine parts. They are strategic components that impact the long-term reliability of CNC automation, industrial robotics, and linear motion systems. Understanding their definition, structure, and applications helps companies make more efficient and reliable decisions in equipment design and purchasing.
If you need more support on linear guides selection and linear motion solutions, please contact Amber or visit IMTEK web.